Causes, Symptoms, and Pathways to Healing:
Depression is more than just feeling sad—it’s a serious mental health condition that affects millions of people around the world. Despite its prevalence, depression is often misunderstood, with many people believing it’s something one can “snap out of” or that it’s simply a case of feeling down. In reality, depression is complex, with deep psychological, biological, and environmental roots.
In this blog, we’ll explore what depression is, its causes, symptoms, and effective ways to manage and heal from this condition.
What Is Depression?

Depression, also known as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in life. While everyone feels low at times, depression is different because it lingers for weeks, months, or even years, affecting daily functioning and quality of life.
It’s important to note that depression is not a sign of weakness or a lack of willpower. It’s a medical condition that requires attention, support, and, often, professional treatment.
Causes of Depression

Depression can arise from a combination of factors. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Biological Factors:
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine can lead to mood disorders.
- Genetics: A family history of depression can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, postpartum, menopause, or thyroid issues can contribute to depression.
2. Psychological Factors:
- Trauma and Stress: Early life trauma, abuse, or a history of chronic stress can create long-lasting effects on mental health.
- Personality: People with certain personality traits, such as low self-esteem or pessimism, may be more prone to depression.
3. Environmental Factors:
- Life Events: Grief, the loss of a loved one, financial problems, or relationship issues can trigger depression.
- Isolation: Lack of social support or prolonged loneliness can contribute to feelings of depression.
Symptoms of Depression
The symptoms of depression can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Persistent Sadness: Feeling sad, empty, or hopeless most of the time.
- Loss of Interest: A lack of enjoyment in activities that used to bring pleasure, such as hobbies, socializing, or even eating.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and low in energy, even after adequate rest.
- Sleep Issues: Insomnia or sleeping too much.
- Appetite Changes: Either a loss of appetite or increased eating, often leading to weight changes.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing, making decisions, or remembering things.
- Irritability: Feeling easily annoyed or frustrated.
- Physical Aches: Unexplained pain, headaches, or digestive problems that don’t seem to have a clear physical cause.
- Feelings of Worthlessness: Excessive guilt or feeling like a burden to others.
- Suicidal Thoughts: In severe cases, thoughts of death or suicide may arise. If these occur, it is critical to seek immediate help from a professional.
Managing and Treating Depression
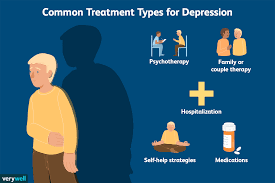
While depression can feel overwhelming, it’s important to remember that it is treatable. There are various paths to healing, and treatment often involves a combination of methods tailored to individual needs.
1. Therapy:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This is a highly effective form of therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to depression.
- Talk Therapy: Speaking with a licensed therapist or counselor can provide emotional support, offer new perspectives, and help manage symptoms.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): Focuses on improving relationships and communication, which can alleviate feelings of isolation and sadness.
2. Medication:
- Antidepressants: These medications, like SSRIs and SNRIs, can help correct chemical imbalances in the brain. They are most effective when taken under the guidance of a doctor and in conjunction with therapy.
3. Lifestyle Changes:
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can boost mood by releasing endorphins, often called “feel-good” hormones. Even a daily walk can make a significant difference.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can improve brain function and mood.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule and improving sleep habits can help regulate mood and energy levels.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can reduce stress and promote mental clarity.
4. Support Networks:
- Family and Friends: Sharing your thoughts and feelings with trusted loved ones can create a sense of connection and support. It also helps to have someone to lean on during difficult times.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group with others who understand what you’re going through can provide validation and encourage healing.
Breaking the Stigma of Depression
One of the most significant barriers to seeking help for depression is the stigma surrounding mental health. Society has made strides in recognizing mental health as important as physical health, but misconceptions and shame still linger. It’s crucial to understand that depression is not a choice or a reflection of personal failure.
By talking openly about depression, supporting mental health awareness, and encouraging others to seek help, we can contribute to breaking the stigma and creating a more compassionate world.
Conclusion
Depression is a challenging condition, but it’s important to remember that healing is possible. Whether through therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or support networks, many pathways to recovery are available. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, don’t hesitate to reach out for help. No one should go through it alone.
Depression doesn’t define who you are—hope, resilience, and recovery are always within reach.


